Have you ever wondered why some businesses seem to effortlessly convert curious visitors into loyal customers while others struggle to make a single sale? The secret often lies in something called a sales funnel. Think of it like dating. You don’t propose marriage on the first date, right? You take time to build trust, understand each other, and gradually move toward commitment. That’s exactly how a sales funnel works in the business world.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear roadmap to guide prospects from curiosity to purchase, just like the most successful brands do.
What is a Sales Funnel?
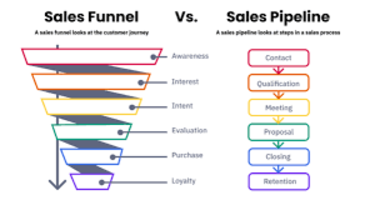
A sales funnel represents the journey potential customers take from first learning about your business to making a purchase decision. Think of an actual funnel: top is broad, while the bottom is narrow. At the top, you have many people who are just discovering your brand. As they move down through different stages, some drop off while others continue toward becoming paying customers.
The beauty of a sales funnel lies in its ability to nurture relationships systematically. Instead of hoping random visitors will buy from you, a well-structured funnel guides them through educational content, builds trust, addresses concerns, and eventually presents the right offer at the right time. Companies like Amazon, Netflix, and Apple have mastered this approach, which is why their conversion rates remain consistently high.
Every business has a sales funnel, whether they’ve intentionally designed one or not. Understanding the different examples of sales funnel models helps you identify what works best for your specific industry and target audience.
What are the 5 Stages of the Sales Funnel?
The traditional sales funnel consists of five distinct stages that mirror the customer’s psychological journey. Each stage requires different messaging, content types, and engagement strategies.
Awareness Stage
This is where potential customers first discover your brand exists. They might find you through social media, search engines, word of mouth, or advertising. At this point, they’re not ready to buy. They’re simply becoming aware that you offer something that might solve their problem. Your goal here is to capture attention and make a memorable first impression.
Interest Stage
Once aware, prospects start showing interest by engaging with your content. They might subscribe to your email list, follow your social media accounts, or browse multiple pages on your website. They’re researching and comparing options. This stage is about providing valuable information that positions you as a helpful expert rather than a pushy salesperson.
Consideration Stage
Now prospects are seriously evaluating whether your solution fits their needs. They’re reading reviews, comparing features, checking prices, and possibly reaching out with questions. This is your opportunity to showcase what makes you different. Case studies, testimonials, free trials, and detailed product demonstrations work exceptionally well here.
Intent Stage
At this stage, prospects have decided they want to buy and are very close to taking action. They might add items to their cart, request a quote, or schedule a consultation. The key is removing any remaining friction points. Clear pricing, easy checkout processes, strong guarantees, and responsive customer support help push them over the line.
Purchase Stage
The final stage is where the transaction happens. But smart businesses know this isn’t really the end. The purchase stage is actually the beginning of a new relationship. Post-purchase communication, onboarding experiences, and follow-up support determine whether this customer becomes a one-time buyer or a repeat customer who refers others.
What six stages make up the sales funnel?
Some marketers prefer a six-stage model that provides more granular insight into customer behavior. This expanded framework adds depth to the traditional approach and helps businesses create more targeted strategies.
Awareness and Discovery
Similar to the awareness stage but with added emphasis on how prospects discover you. Different discovery channels require different approaches. Someone who finds you through Google search has different expectations than someone who sees your Instagram ad.
Interest and Engagement
This stage focuses specifically on active engagement metrics. Are prospects opening your emails? Watching your videos? Downloading your resources? Having quality engagement is better than lots of engagements.
Evaluation and Research
Here prospects are actively comparing you against competitors. They’re digging deeper into specifications, pricing structures, and customer experiences. Competitive comparison guides and transparent communication work powerfully at this stage.
Decision and Intent
Prospects have narrowed their choices and are ready to decide. Limited-time offers, consultations, personalized recommendations, and clear calls to action help convert intent into action.
Purchase and Transaction
The actual buying moment requires seamless execution. Any technical glitches, confusing processes, or unexpected costs can derail the sale even at this late stage.
Loyalty and Advocacy
This often-overlooked stage focuses on turning customers into brand advocates. Satisfied customers who recommend your business to others become your most valuable marketing asset. Loyalty programs, referral incentives, and exceptional ongoing support nurture this relationship.
Real-World Examples of Sales Funnel
Understanding theory is important but seeing how successful businesses implement sales funnels brings the concept to life. Let’s explore several proven examples of sales funnel strategies across different industries.
E-commerce Product Funnel
Online retailers like fashion brands use a straightforward but effective funnel. A potential customer sees an Instagram ad featuring a stylish jacket. Clicking through takes them to a landing page with high-quality images and customer reviews. An exit-intent popup offers a discount code for first-time buyers when they’re about to leave.
If they don’t purchase immediately, retargeting ads follow them across the web. Abandoned cart emails remind them about the jacket sitting in their cart, sometimes with an additional incentive. This systematic approach turns casual browsers into buyers.
Software as a Service Funnel
SaaS companies often use the ‘freemium’ model as their funnel foundation. Users discover the tool through content marketing or recommendations. They sign up for a free trial or basic plan without entering payment information. During the trial, educational emails demonstrate key features and showcase success stories.
In-app messages highlight premium features they’re missing. As they approach usage limits on the free plan, targeted upgrade prompts appear. This gradual exposure allows users to experience value before committing financially.
Lead Magnet Funnel
Service providers like consultants, coaches, and agencies frequently use lead magnets. A prospect searching for marketing advice finds a comprehensive guide offered in exchange for their email address. The guide provides genuine value while demonstrating expertise.
Follow-up emails continue providing helpful tips while subtly mentioning services. Eventually, recipients receive an invitation to a free strategy session. During this session, the consultant identifies specific needs and presents a customized service proposal. This funnel builds trust before asking for significant investment.
Webinar Funnel
Educational webinars serve as powerful funnel mechanisms for higher-ticket products or services. Prospects register for a free training session on a topic they care about. Reminder emails ensure good attendance. The webinar delivers solid educational content while naturally leading to how the host’s product or service provides the complete solution. A special offer available only to attendees creates urgency.
Post-webinar follow-up sequences address common objections and provide additional resources. This approach combines education with selling in a non-pushy way.
Content Marketing Funnel
Businesses using content marketing create funnels through valuable information. A prospect searches for how to solve a specific problem and finds a detailed blog post. That post includes links to related articles and a subscription option for more tips.
Email subscribers receive a series of increasingly advanced content pieces. Eventually, this content naturally transitions to how the company’s product or service provides the ultimate solution. This funnel works slowly but builds deep trust and attracts highly qualified leads.
Tripwire Funnel
This strategy uses a low-priced introductory offer to convert prospects into customers. A fitness brand might offer a one-week meal plan for just a few dollars. This small commitment gets prospects past the psychological barrier of making their first purchase.
Buyers then receive upsell offers for monthly subscriptions, personal coaching, or premium programs. The initial low-risk purchase proves the quality and builds confidence for larger investments.
How do I Create a Sales Funnel?
Building an effective sales funnel doesn’t require expensive tools or marketing expertise. Following a systematic approach allows anyone to create a funnel that generates consistent results.
Identify Your Target Audience
Start by getting crystal clear about who you’re serving. What problems do they face? Where do they spend time online? What objections might prevent them from buying? The better you understand your ideal customer, the more effectively you can craft messaging that resonates. Create detailed customer personas that guide all your funnel decisions.
Map the Customer Journey
Walk through the steps someone takes from never hearing about you to becoming a customer. What questions do they have at each stage? What information do they need? Where might they get stuck? This exercise reveals gaps in your current approach and opportunities to smooth the path to purchase.
Create Awareness Assets
Develop content that attracts your target audience’s attention. This might include blog posts optimized for search engines, social media content, paid advertising, podcasts, videos, or guest appearances on other platforms. Focus on providing genuine value rather than immediate selling. Your goal is simply to get noticed by the right people.
Develop Interest-Building Content
Once you have attention, you need to maintain interest and build credibility. Email newsletters, video series, free courses, and interactive tools keep prospects engaged while demonstrating your expertise. This middle stage is where trust develops, so consistency and quality matter tremendously.
Design Conversion Mechanisms
Create specific touchpoints where interested prospects can take the next step. This might be scheduling a call, starting a free trial, requesting a quote, or making a purchase. Remove as much friction as possible from these conversion points. Simple forms, clear instructions, and obvious benefits increase conversion rates.
Implement Follow-Up Systems
Many sales happen in the follow-up, not the initial contact. Automated email sequences, retargeting ads, and strategic outreach keep you present without being annoying. Different prospects move at different speeds, so having multiple touchpoints accommodates various decision-making timelines.
Optimize and Improve
Track metrics at each funnel stage to identify where prospects drop off. Test different headlines, offers, email sequences, and landing page designs. Small improvements compound over time into significantly better results. The most successful funnels evolve based on real performance data rather than assumptions.
Essential Tools for Building Your Sales Funnel
While you can build basic funnels with simple tools, specialized platforms streamline the process and provide powerful features.
Email Marketing Platforms
Services like Mailchimp, ConvertKit, or ActiveCampaign let you capture leads, send automated sequences, and segment your audience based on behavior. Email remains one of the highest-converting channels for moving prospects through your funnel.
Landing Page Builders
Tools like Leadpages, Unbounce, or Instapage help create focused pages designed specifically for conversion. Unlike regular website pages, landing pages eliminate distractions and guide visitors toward a single action.
Customer Relationship Management Systems
CRM platforms like HubSpot, Salesforce, or Pipedrive organize prospect information and track interactions. For businesses with longer sales cycles, CRMs ensure no opportunity falls through the cracks.
Analytics and Tracking
Google Analytics, Hotjar, and similar tools show exactly how visitors interact with your funnel. Understanding where people spend time, where they leave, and what they click reveals optimization opportunities.
All-in-One Funnel Platforms
Solutions like ClickFunnels, Kartra, or Systeme.io combine multiple tools into integrated systems. While potentially more expensive, they eliminate technical headaches and provide pre-built funnel templates.
Common Sales Funnel Mistakes to Avoid
Even well-intentioned marketers make errors that sabotage their funnel performance. Avoiding these common pitfalls improves your results significantly.
Asking for Too Much Too Soon
Requesting a major commitment before building trust rarely works. Would you invest thousands of dollars with a company you just discovered? Neither will your prospects. Build relationships gradually through the funnel stages.
Ignoring Mobile Experience
Mobile devices account for almost half of all website traffic. If your funnel doesn’t work smoothly on smartphones, you’re losing huge numbers of potential customers. Test every step on multiple devices and screen sizes.
Neglecting Follow-Up
Most prospects don’t buy on first contact. Without systematic follow-up, you’re leaving money on the table. Automated sequences keep you present in prospects’ minds without requiring constant manual effort.
Creating Confusing Paths
Every funnel stage should have one clear next step. Multiple competing calls to action confuse prospects and reduce conversion rates. Simplicity converts better than complexity.
Forgetting About Existing Customers
The most expensive customer is the next one. The most profitable is often the one you already have. Funnels shouldn’t end at purchase. Creating pathways for repeat purchases, upsells, and referrals maximizes customer lifetime value.
Measuring Sales Funnel Success
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Tracking specific metrics reveals funnel performance and guides optimization efforts.
Conversion Rate by Stage
Calculate what percentage of prospects move from each stage to the next. If you have a high drop-off at a particular point, you’ve identified where to focus improvement efforts.
Customer Acquisition Cost
Divide the total amount of money you spend on sales and marketing by the quantity of new clients you bring on board. This reveals whether your funnel is economically sustainable and profitable.
Average Order Value
Track how much customers typically spend. Strategies that increase this number without increasing acquisition costs directly boost profitability.
Time to Conversion
Measure how long prospects typically take to move through your funnel. This information helps set realistic expectations and informs follow-up timing.
Customer Lifetime Value
Calculate the total revenue you expect from a customer relationship over time. This metric justifies how much you can afford to spend on acquisition while remaining profitable.
FAQs
How long should a sales funnel be?
Sales funnel length varies dramatically based on your product, price point, and industry. Low-cost impulse purchases might have funnels that convert in minutes, while enterprise software sales could take months. B2C funnels for products under one hundred dollars typically range from a few days to a few weeks.
B2B funnels or high-ticket coaching programs often span several weeks to months. The key is matching funnel length to your customer’s natural decision-making timeline rather than rushing them or dragging things out unnecessarily.
What distinguishes a marketing funnel from a sales funnel?
While often used interchangeably, these terms can have subtle differences. A marketing funnel focuses on the awareness and interest stages, concentrating on attracting and engaging prospects. A sales funnel encompasses the entire journey including the decision and purchase stages where direct selling occurs.
Think of the marketing funnel as feeding qualified leads into the sales funnel. In practice, modern approaches integrate both into a seamless customer journey, making the distinction less important than ensuring all stages work together effectively.
Can small businesses benefit from sales funnels?
Absolutely, and arguably small businesses benefit even more than large corporations. With limited resources, small businesses can’t afford to waste marketing effort on unqualified leads or inefficient processes. A well-designed funnel focuses resources on prospects most likely to convert.
Even simple funnels with basic email sequences and landing pages dramatically outperform scattershot marketing approaches. Many small businesses start with one straightforward funnel and expand as they see results.
What is the price of creating a sales funnel?
You can build a basic but functional sales funnel for free using tools like Mailchimp’s free plan, WordPress, and Google Analytics. More sophisticated funnels with paid advertising, premium email platforms, landing page builders, and automation tools might run from fifty to several hundred dollars monthly.
Custom-built funnels with development work and extensive paid traffic could cost thousands. The investment should match your business size and expected return. Start simple and scale up as you prove the concept works for your specific situation.
How often should I update my sales funnel?
Your funnel needs regular attention but not constant overhaul. Review performance metrics monthly to identify trends and problem areas. Make minor optimizations like tweaking email copy or testing new headlines regularly. Conduct more substantial reviews quarterly to assess whether the overall structure still aligns with customer behavior and business goals.
Major funnel redesigns should happen when you significantly change your product offering, target a new audience, or notice performance declining despite optimization efforts. The key is continuous improvement rather than either neglecting the funnel or changing it so frequently that you can’t measure what actually works.
Conclusion
Understanding examples of sales funnel strategies and implementing them effectively can transform your business results. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to optimize existing processes, a well-structured sales funnel guides prospects from curiosity to purchase systematically and profitably. The most successful funnels share common characteristics.
They understand their audience deeply, provide genuine value at every stage, remove friction from the buying process, and nurture relationships beyond the initial purchase. Examples of sales funnel models from e-commerce, SaaS, service providers, and content marketers demonstrate that the principles adapt across industries while the specific tactics vary based on your unique situation.
Start by mapping your current customer journey and identifying gaps where prospects fall away. Choose one funnel type that aligns with your business model and audience preferences. Build it simply at first, measure results carefully, and optimize based on real data rather than assumptions.
The question isn’t whether you need a funnel, but rather which funnel structure will serve your specific audience most effectively. Act today to design a funnel that turns curious visitors into loyal customers consistently and predictably.